

Engine control unit (ECU) - not to be confused with electronic control unit, the generic term for all these devices.The engine controller may have several different names, such as "DME", "Enhanced Powertrain", "PGM-FI" and many others. Other Controllers All other controller names are decided upon by the individual OEM.Generic Powertrain The Generic Powertrain pertains to a vehicles emission system and is the only regulated controller name.
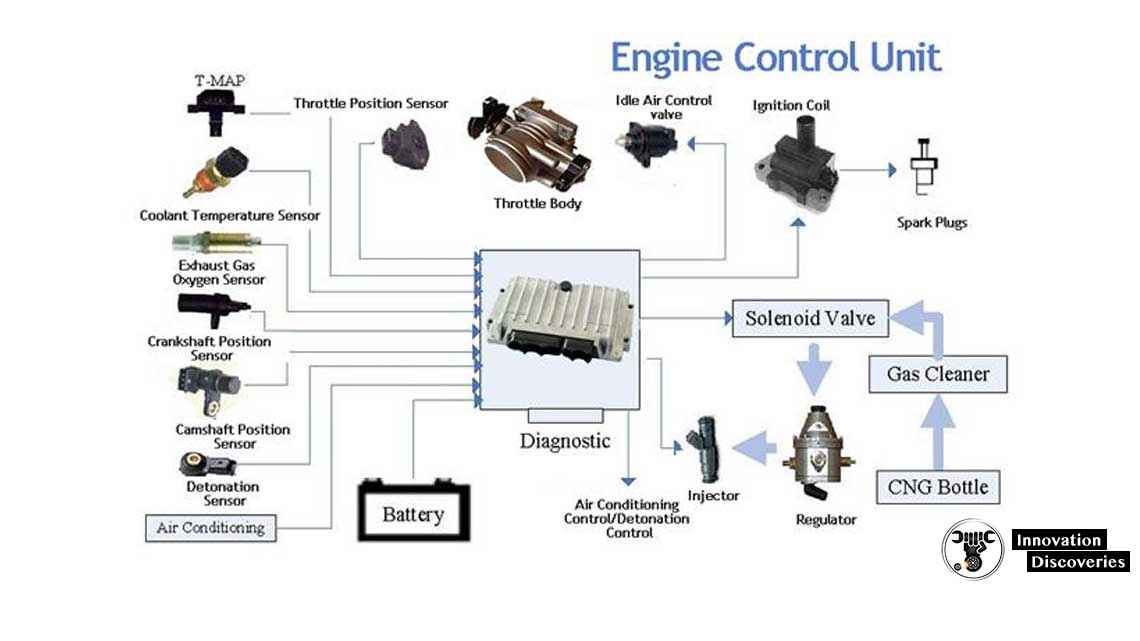
Generic Industry Controller Naming - Is the naming of controllers where the logical thought of the controller's name implies the system the controller is responsible for controlling.
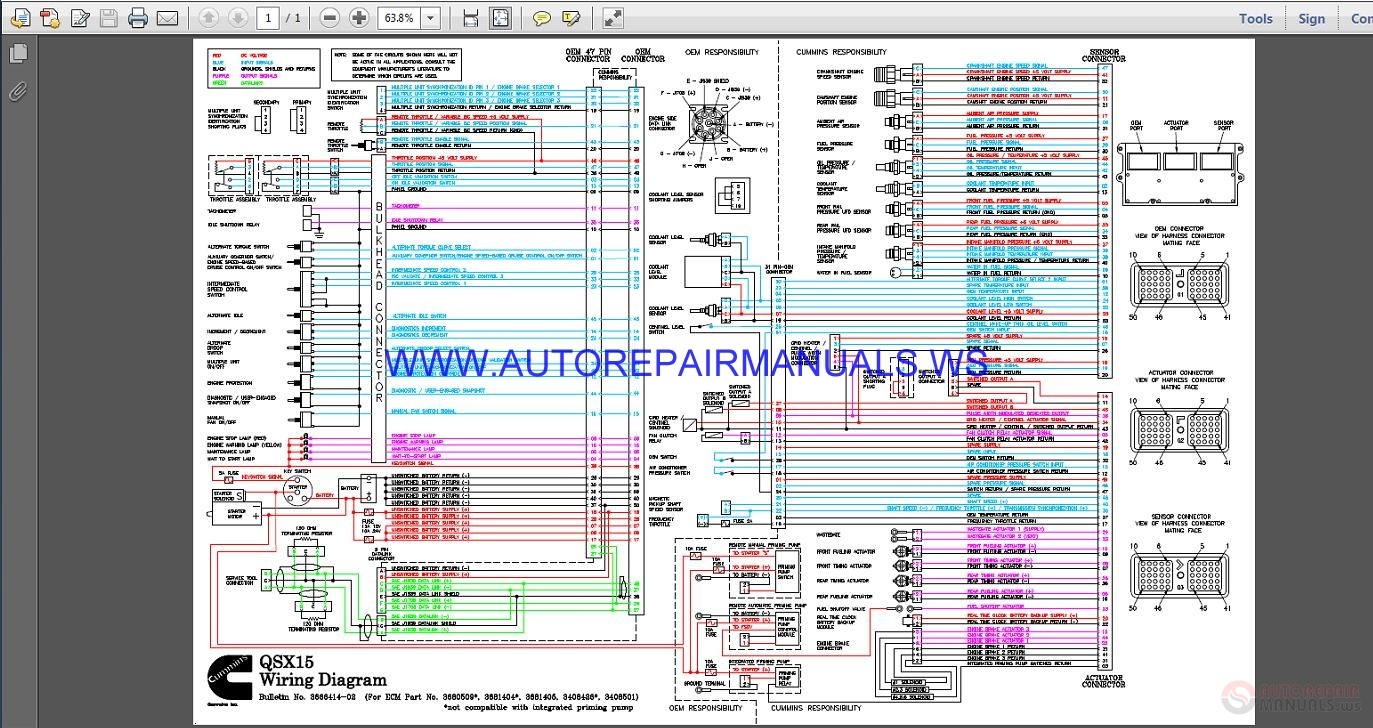
Managing the increasing complexity and number of ECUs in a vehicle has become a key challenge for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Embedded software in ECUs continues to increase in line count, complexity, and sophistication. Some modern motor vehicles have up to 150 ECUs. Sometimes an assembly incorporates several individual control modules (a PCM often controls both the engine and the transmission). These ECUs together are sometimes referred to collectively as the car's computer though technically they are all separate computers, not a single one. Modern vehicles have many ECUs, and these can include some or all of the following: engine control module (ECM), powertrain control module (PCM), transmission control module (TCM), brake control module (BCM or EBCM), central control module (CCM), central timing module (CTM), general electronic module (GEM), body control module (BCM), and suspension control module (SCM). An electronic control unit ( ECU), also known as an electronic control module ( ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
